What Are the Examples of Factory Automation
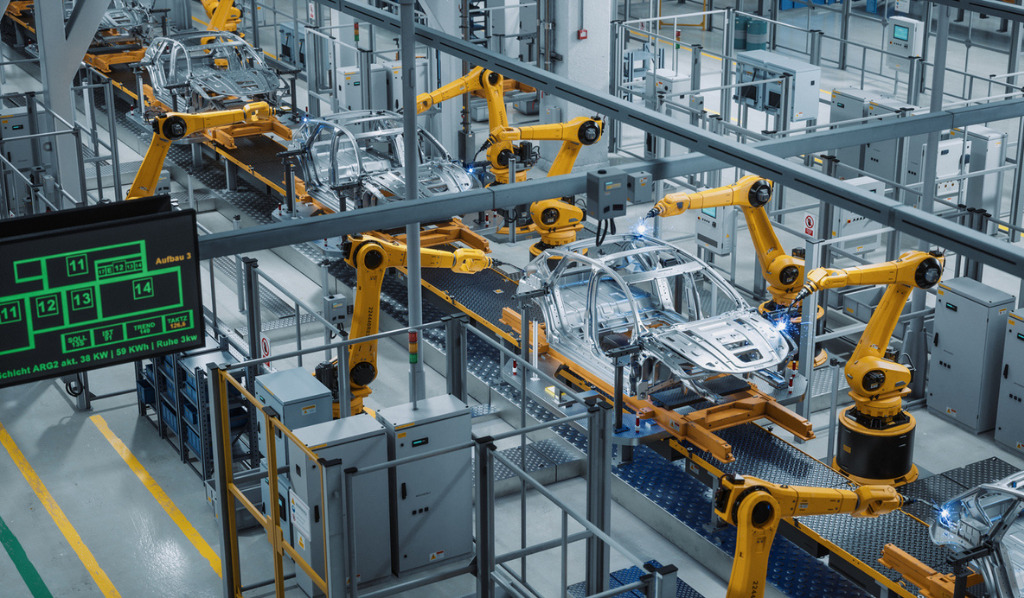

Step into the era of automation, where factories are liberated from manual labor and monotonous procedures. The incorporation of factory automation has transformed the manufacturing sector, enhancing operations, increasing effectiveness, and unlocking unparalleled levels of productivity. From tireless robotic arms assembling goods to autonomous systems making independent decisions, the potential is boundless.
This blog post delves into the realm of factory automation and presents captivating examples that demonstrate its capabilities and possibilities. Buckle up as we embark on an exhilarating excursion through the world of automated factories!
Contents
Evolution of Factory Automation
The evolution of factory automation can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, signaling a shift from manual labor to mechanization. Steam-powered machines and assembly lines marked early milestones, enhancing efficiency. The 20th century brought electrical systems, paving the way for automated conveyor belts and specialized machinery.
A significant shift occurred in the late 20th century with the integration of computers and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), enabling real-time monitoring and control. Today, we are in a new phase propelled by robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), ushering in smarter and more autonomous factories. The future envisions increased collaboration between humans and machines, with collaborative robots (cobots) boosting productivity alongside human workers.
AI algorithms are set to optimize production schedules in real time. This transformative landscape positions factory automation as a pivotal component for businesses seeking a competitive edge globally. Strategic adoption of technological advancements allows manufacturers to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, cost savings, and innovation, propelling their operations into a future defined by the seamless integration of human and machine capabilities.
Benefits of Factory Automation
Factory automation has brought about numerous benefits, transforming manufacturing processes and revolutionizing the industry. Some key advantages include:
- Increased Productivity: Automated systems enable faster task execution with higher precision, reducing human error and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: Automation leads to savings on labor costs by minimizing the need for human intervention in repetitive tasks. It also contributes to accurate inventory control and reduces material waste, resulting in substantial cost savings.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Automated processes ensure consistency and accuracy in production, minimizing variations introduced by human factors. This results in higher-quality products that consistently meet stringent standards.
- Improved Worker Safety: Automation eliminates or reduces exposure to hazardous conditions and physically demanding tasks, contributing to a safer working environment for employees. Robots and machines take on potentially dangerous roles.
- Scalability: Automated systems facilitate easy scalability for businesses. As demand increases, these systems allow for seamless expansion without compromising efficiency or product quality.
The implementation of factory automation is a strategic investment for manufacturers aiming to remain competitive in today’s dynamic market. The benefits derived from automation contribute significantly to increased productivity, cost-effectiveness, product quality, worker safety, and the overall scalability of manufacturing operations.
Top Examples of Factory Automation
Automation in factories has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, streamlining processes and increasing efficiency. Here are some top examples of factory automation that have made a significant impact:
Top 1: Robotics and Robotic Arms
Robotics and Robotic Arms have revolutionized factory automation by taking over tasks previously performed by humans. Equipped with sensors and advanced algorithms, they perform complex movements with precision, offering advantages like increased productivity and worker safety.
Top 2: Automated Assembly Lines
Automated Assembly Lines have revolutionized manufacturing, streamlining processes in industries such as automotive and electronics. These systems, equipped with robots, enhance efficiency and product quality by performing tasks like welding and intricate component placement.
Top 3: Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT Integration has transformed factory operations by connecting machines and sensors. Smart sensors collect real-time data for predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and remote monitoring, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Top 4: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems
AI systems in factory automation, such as predictive maintenance and quality control, mimic human intelligence. These systems optimize inventory management and employ AI-powered robots for precise and adaptive tasks.
Top 5: Machine Learning Applications
Machine Learning Applications in factory automation enable machines to learn and improve without explicit programming. They contribute to predictive maintenance, automated quality control, optimized production workflows, and adaptive robotic systems, promising continuous advancements.
Future Trends in Factory Automation
As technology rapidly advances, the future of factory automation holds exciting trends:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots will be more prevalent, working alongside humans with easy programmability for various tasks. They enhance flexibility, efficiency, and ensure human worker safety.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI’s role will significantly expand, with smarter machine learning algorithms analyzing real-time data. This optimization will enhance production processes and proactively identify potential issues.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion: IoT devices will continue to grow within factories, fostering seamless communication between machines. This connectivity allows for enhanced monitoring, control, and improved efficiency, reducing downtime.
- 3D Printing Revolution: Additive manufacturing or 3D printing will revolutionize prototyping and small-scale production in factory automation. Quick and precise production of custom parts is a key potential.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA will automate repetitive tasks through software robots, streamlining administrative processes like data entry or order processing efficiently.
These trends offer a glimpse into the future of factory automation, driven by ongoing innovation and technological advancements.
Challenges and Mitigations
factory automation presents significant benefits, but it also comes with challenges and limitations:
Challenges
- High Initial Investment: The substantial cost of implementing automated systems, including robotics, assembly line equipment, IoT devices, AI, and machine learning applications, poses a financial challenge for companies.
- Technical Expertise: Operating and maintaining automated systems requires specialized technical expertise. Companies may need to invest in employee training or hire personnel with the necessary skills.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating diverse automation technologies from different vendors can be complex and time-consuming. Compatibility issues between hardware and software components may require additional troubleshooting efforts.
- Limitations in Customization: Automated systems may struggle with customization for intricate or unique processes that require human intervention or adaptability beyond their programmed capabilities.
- Job Displacement Concerns: The increased automation of tasks raises concerns about job displacement, potentially leading to job loss among workers who performed manual tasks now automated.
Mitigations
Despite these challenges, companies can navigate the landscape effectively by:
- Strategic Planning: Carefully considering factors such as costs, technical expertise, and integration challenges during the planning stages of automation implementation.
- Strategic Technological Adoption: Leveraging technological advancements strategically to maximize benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
- Investment in Training: Prioritizing investment in employee training or hiring skilled personnel to ensure efficient operation and maintenance of automated systems.
- Vendor Collaboration: Engaging in effective collaboration with automation technology vendors to streamline integration and address compatibility issues.
- Balancing Automation and Human Intervention: Recognizing the limitations of automation and finding a balance between automated processes and tasks that require human intervention or adaptability.
By approaching factory automation with a thoughtful and strategic mindset, companies can overcome these challenges and create a more efficient, productive, and sustainable manufacturing environment.
Conclusion: The Impact and Importance of Factory Automation
In conclusion, the integration of robotics, AI, machine learning, IoT, and automated assembly lines in factory automation has ushered in a transformative era for industries worldwide. This evolution enhances efficiency, ensures safety, and cuts costs, reshaping global manufacturing processes. As businesses streamline operations to meet growing demands, automation becomes a cornerstone of competitiveness.
Challenges, including initial costs and job displacement concerns, can be addressed through strategic implementation, robust training initiatives, and meticulous maintenance strategies. The continuous evolution of technology promises even more significant advancements, propelling us into an era where the boundaries of automation redefine the possibilities in our highly automated world.