What Are the Components of a Commercial Solar System?
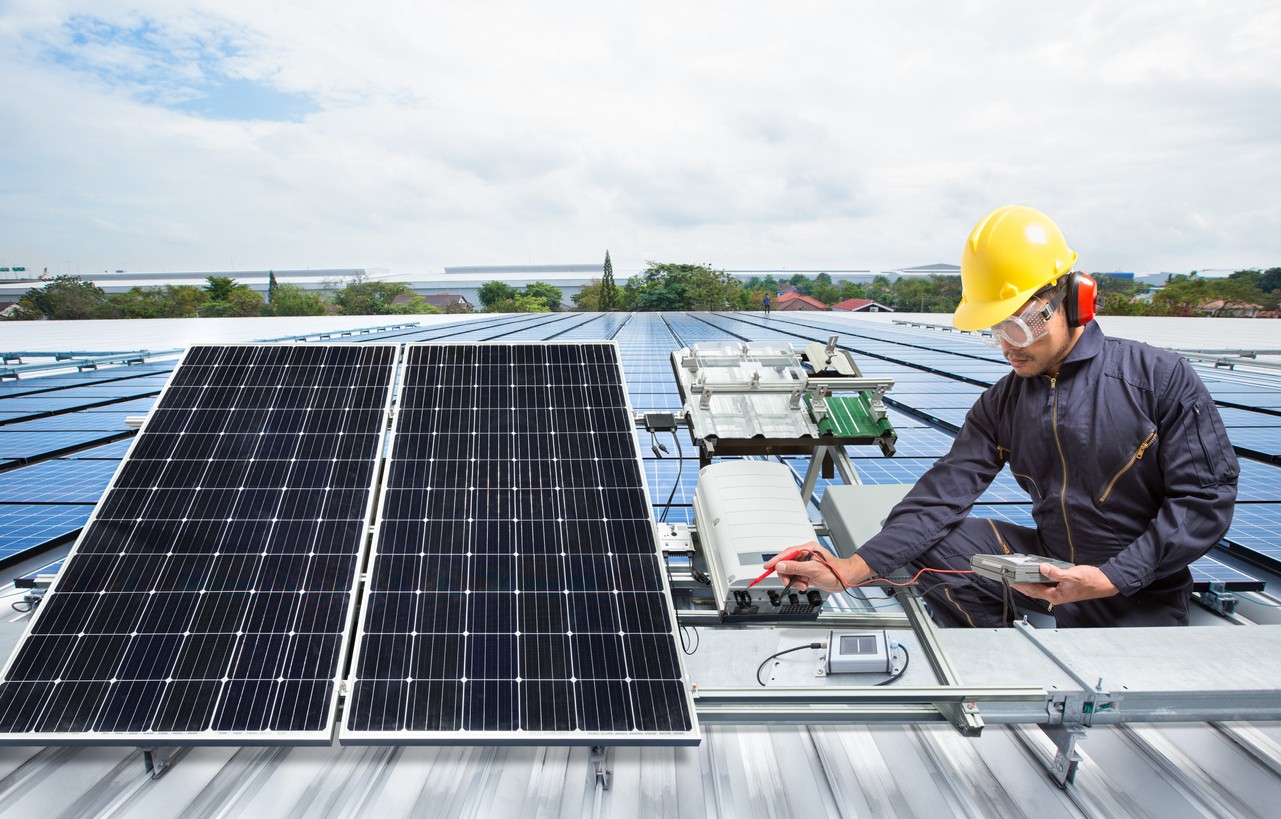

As businesses and industries increasingly embrace renewable energy solutions, commercial solar systems have become famous for lessening carbon footprints, cutting energy costs, and demonstrating corporate social responsibility. A commercial solar system is a large-scale installation that harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity, supplying a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional energy sources. We will explore the elementary components of a commercial solar system, their functions, and how they function together to enable businesses to generate clean energy efficiently.
Contents
Components of a commercial solar system
- Solar Panels
The cornerstone of any solar system is the solar panels, also comprehended as photovoltaic (PV) modules. These panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. Solar panels are typically made of silicon-based semiconductor materials. When sunlight strikes their surface, the photons from the sunlight knock electrons loose from their atoms, generating an electrical current.
Commercial solar systems consist of numerous solar panels linked together to assemble arrays. The number of solar panels and their arrangement lean on the system’s size and the available space on the commercial property. Two popular types of solar panels utilized in commercial systems are monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
- Mounting Structure
The mounting structure is a paramount component that ensures the stability and optimal positioning of the solar panels. Commercial solar systems require robust and durable mounting systems capable of withstanding weather conditions, including strong winds, rain, and snow. There are diverse sorts of mounting structures, such as fixed-tilt mounts, which are stationary at a precise angle, and tracking mounts, which automatically adjust the tilt and orientation of the panels to track the sun’s path throughout the day. While tracking mounts can improve energy generation, they are more complex and costly than fixed-tilt mounts.
- Solar Inverters
Solar inverters play a paramount role in a commercial solar system by altering the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, the electricity most electrical appliances use, and the power grid. AC electricity is more fitting for transmitting electricity over long distances and for use in commercial and industrial settings.
There are several types of solar inverters used in commercial systems, including:
- String Inverters: These inverters are commonly used in smaller commercial systems. They connect multiple solar panels in a “string” and convert the combined DC electricity from the string into AC electricity.
- Central Inverters: Ideal for larger commercial installations, central inverters can handle a higher power output. They convert the DC electricity from all the solar panels in the system into AC electricity.
- Microinverters: Microinverters are installed on each solar panel, converting the DC electricity at the panel level into AC electricity. This configuration allows for individual panel optimization and monitoring, improving overall system performance.
- Power Optimizers: Power optimizers work with string inverters to optimize the performance of each panel individually.
Energy Storage Systems
While only sometimes a standard component of commercial solar systems, energy storage systems (ESS) are becoming increasingly popular for businesses seeking to maximize the advantages of their solar installations. ESS consists of batteries that store excess energy generated by solar panels during sunny periods. In times of low energy production or high demand, such as cloudy days or peak hours, the stored energy can power the business operations or even feed surplus electricity back into the grid. This enhances energy independence for the business and helps stabilize the grid by lowering demand during peak hours.
Monitoring and Control Systems
Monitoring and control systems are paramount to ensure a commercial solar system’s optimal performance and efficiency. These systems deliver real-time data on energy production, consumption, and system health, enabling businesses to detect and handle any issues. Monitoring and control systems authorize solar system operators to pinpoint problems such as malfunctioning panel, inverter issues, or wiring faults. Additionally, they enable performance tracking over time, which helps businesses assess the return on investment and make informed decisions about system maintenance and upgrades.
Grid Connection and Net Metering
Most commercial solar systems are interconnected with the local electrical grid. When the solar system generates more electricity than the business consumes, the surplus energy is fed back into the grid. This process is facilitated through net metering or feed-in tariff programs, depending on the region’s regulations. Net metering allows businesses to receive credits for the excess electricity they contribute to the grid, which can offset the electricity they consume when the solar system doesn’t generate sufficient power (e.g., at night or on cloudy days). This mechanism ensures a cost-effective and reliable energy supply for commercial enterprises while promoting the adoption of renewable energy.
Commercial solar systems from a professional company such as Solar Peak are an environmentally sustainable and economically beneficial solution for businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs. The components of a commercial solar system, including solar panels, mounting structures, inverters, energy storage systems, monitoring systems, and grid interconnection mechanisms, work together harmoniously to generate clean electricity and enable businesses to operate in an eco-friendly manner. You can learn more about Solar Peak here.